流程如下:
- 先使用 Filebeat 把日志收集起来,然后把数据再传给 Logstash。
- 通过 Logstash 强大的数据清洗功能。
- 最终把数据写入到 Elasticsearch 中。
- 并由 Kibana 进行可视化
参考文档:
https://www.51cto.com/article/707776.html
踩的坑:
- 指定配置文件启动
安装nc
sudo dnf install -y nc
nc -h
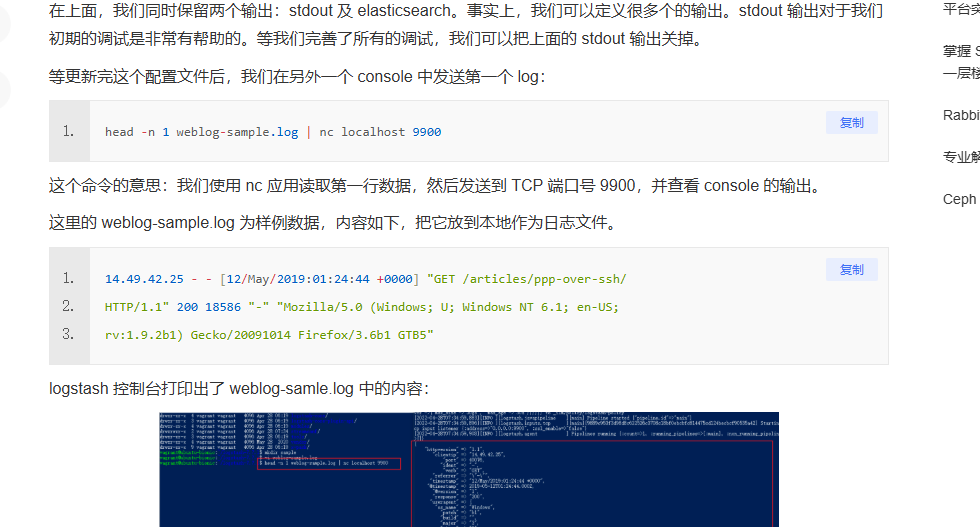
bin/logstash -f /logstash-7.7.1/streamconf/weblog.conf
- 脚本文件
先转化为unix系统的脚本文件
sudo yum install dos2unix # 对于 CentOS 或 RHEL 系统
dos2unix start.sh
# nohup bin/logstash -f streamconf/weblog.conf &
#!/bin/bash
# Logstash 配置文件路径
CONFIG_PATH="streamconf/weblog.conf"
# 查找 Logstash 进程的 PID
PID=$(ps aux | grep "logstash" | grep -v "grep" | awk '{print $2}')
# 如果有 Logstash 进程在运行,则先杀死它
if [ ! -z "$PID" ]; then
echo "发现 Logstash 进程 (PID: $PID),正在停止..."
kill -9 $PID
echo "Logstash 进程已停止。"
else
echo "没有发现 Logstash 进程。"
fi
# 启动 Logstash
echo "启动 Logstash..."
nohup bin/logstash -f $CONFIG_PATH &
echo "Logstash 启动命令已执行,后台运行中..."
# tail -f -n 30 nohup.out
配置文件
logstash
weblog.conf
input {
beats {
port => "9900" # 接收 Filebeat 日志的端口
}
}
filter {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{COMBINEDAPACHELOG}" }
}
mutate {
convert => { "bytes" => "integer" }
}
geoip {
source => "clientip"
}
useragent {
source => "user_agent"
target => "useragent"
}
date {
match => ["timestamp", "dd/MMM/yyyy:HH:mm:ss Z"]
target => "@timestamp"
}
if [level] == "stat" {
drop { }
}
}
output {
# 输出到 Elasticsearch,根据 index_prefix 动态生成索引
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["localhost:9200"]
user => "elastic"
passsword => "xxx"
index => "%{index_prefix}" # 动态索引
}
# 输出到控制台(调试用,可选)
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}
start.sh
# nohup bin/logstash -f streamconf/weblog.conf &
#!/bin/bash
# Logstash 配置文件路径
CONFIG_PATH="streamconf/weblog.conf"
# 查找 Logstash 进程的 PID
PID=$(ps aux | grep "logstash" | grep -v "grep" | awk '{print $2}')
# 如果有 Logstash 进程在运行,则先杀死它
if [ ! -z "$PID" ]; then
echo "发现 Logstash 进程 (PID: $PID),正在停止..."
kill -9 $PID
echo "Logstash 进程已停止。"
else
echo "没有发现 Logstash 进程。"
fi
# 启动 Logstash
echo "启动 Logstash..."
nohup bin/logstash -f $CONFIG_PATH &
echo "Logstash 启动命令已执行,后台运行中..."
tail -f -n 30 nohup.out
filebeat
filebeat_apache.yml
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /xxx1/xxx/server/xxx2/log/**/*.log
- /xxx1/xxx/server/xxx2/logslave/**/*.log
fields:
index_prefix: "test-xx-xxx2" # 设置 Index 前缀
fields_under_root: true # 将自定义字段放到顶层
ignore_older: 360h # 忽略超过 24 小时的日志(根据需求调整)
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
# - /xxx1/gozero/wann-user-api/log/*.log
- /xxx1/gozero/wann-user-api/**/*.log
fields:
index_prefix: "test-xx-user-api" # 设置 Index 前缀
fields_under_root: true
ignore_older: 360h
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
# - /xxx1/gozero/wann-user-api/log/*.log
- /xxx1/gozero/wann-operation-api/**/*.log
fields:
index_prefix: "test-xx-operation-api" # 设置 Index 前缀
fields_under_root: true
ignore_older: 360h
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /xxx1/xxx/server/admin/log/**/*.log
fields:
index_prefix: "test-xx-admin" # 设置 Index 前缀
fields_under_root: true
ignore_older: 360h
# output.elasticsearch:
# hosts: ["http://ip:9200"]
output.logstash:
hosts: ["ip:9900"] # 将日志发送到 Logstash
start.sh
# nohup ./filebeat -e -c filebeat_apache.yml &
#!/bin/bash
# Filebeat 配置文件路径
CONFIG_PATH="filebeat_apache.yml"
# 查找 Filebeat 进程的 PID
PID=$(ps aux | grep "filebeat" | grep -v "grep" | awk '{print $2}')
# 如果有 Filebeat 进程在运行,则先杀死它
if [ ! -z "$PID" ]; then
echo "发现 Filebeat 进程 (PID: $PID),正在停止..."
kill -9 $PID
echo "Filebeat 进程已停止。"
else
echo "没有发现 Filebeat 进程。"
fi
# 启动 Filebeat
echo "启动 Filebeat..."
# nohup ./filebeat -e -c $CONFIG_PATH &
# nohup ./filebeat -e -c $CONFIG_PATH & disown
nohup ./filebeat -e -c filebeat_apache.yml & disown
# nohup ./filebeat -e -c $CONFIG_PATH > filebeat.log 2>&1 &
echo "Filebeat 启动命令已执行,后台运行中..."
# tail -f -n 30 nohup.out
es
elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: "my-es"
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
xpack.security.enabled: true
kibana
kibana.yml
# Default Kibana configuration for docker target
server.name: kibana
server.host: "0"
elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://172.17.0.3:9200"]
xpack.monitoring.ui.container.elasticsearch.enabled: true
elasticsearch.username: "elastic"
elasticsearch.password: "password"
成品展示
配置开机自启
vim /etc/rc.local
# 加入文件绝对路径
设置登录密码
要在 Docker 环境中为您的 Elasticsearch 和 Kibana(版本 7.7.1)设置登录密码:
-
启用 Elasticsearch 安全功能:
-
Elasticsearch 默认未启用安全功能。要启用它,您需要修改
elasticsearch.yml配置文件。 -
首先,进入运行中的 Elasticsearch 容器:
docker exec -it <elasticsearch_container_name> /bin/bash -
然后,编辑
config/elasticsearch.yml文件,添加以下内容:xpack.security.enabled: true这将启用 Elasticsearch 的安全功能。
-
保存文件并退出编辑器后,退出容器并重启 Elasticsearch 容器使配置生效:
exit docker restart <elasticsearch_container_name>
-
-
设置内置用户密码:
-
在启用安全功能后,您需要为内置用户设置密码。再次进入 Elasticsearch 容器:
docker exec -it <elasticsearch_container_name> /bin/bash -
运行以下命令以交互方式设置内置用户的密码:
./bin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords interactive按照提示,为每个内置用户(如
elastic、kibana等)设置密码。
-
-
配置 Kibana:
-
Kibana 需要使用已设置的用户名和密码来连接 Elasticsearch。编辑 Kibana 的配置文件
kibana.yml。 -
首先,进入运行中的 Kibana 容器:
docker exec -it <kibana_container_name> /bin/bash -
编辑
config/kibana.yml文件,添加以下内容:elasticsearch.username: "kibana" elasticsearch.password: "<kibana_user_password>"将
<kibana_user_password>替换为您在前一步中为kibana用户设置的密码。 -
保存文件并退出编辑器后,退出容器并重启 Kibana 容器使配置生效:
exit docker restart <kibana_container_name>
-
-
验证配置:
-
在浏览器中访问 Kibana 的 URL(通常为
http://<your_host>:5601)。 -
此时,Kibana 应提示您输入用户名和密码。使用
elastic用户名和您之前设置的密码进行登录。
-



评论区